62. Chemical Components and Analysis 5
- INDEX -
Acidity (Fat acidity, Water soluble acidity)
Determination of Fat Acidity by Titration Method
Determining Fat Acidity by Colorimetric Method
Water Soluble Acidity
Acidity (Fat Acidity, Water Soluble Acidity)
Of all the major elements of rice, lipid dissolution progresses faster than that of protein and starch during storage, which makes fat acidity (expression in mg of the volume of potassium hydroxide required to neutralize free fatty acid contained within 100g of cereal powder) the most commonly used index of quality deterioration for rice.
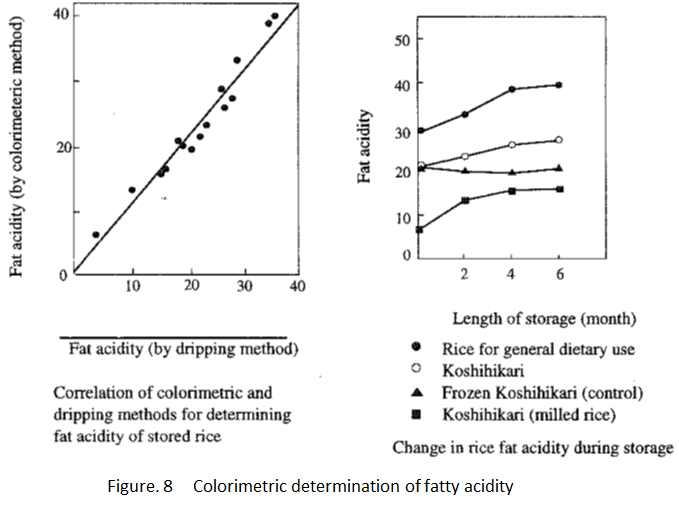
The traditional method was to drip potassium hydroxide until the free fatty acid extracted from the sample was neutralized. The problem with this method was that it relies on visual observations and it is difficult to determine when to stop dripping. Ohtsubo (Food Research Institute) have developed a colorimetric method of determining fat acidity using a highly sensitive determination method for copper salt of organic acid. They applied it to the quality test for stored rice and found the colorimetric method has a high correlation with the traditional method )dripping method), and is useful for determining minute changes in milled rice during storage. (Fig. 8).
Determination of Fat Acidity by Titration Method
1) Breaking down and measuring the sample: Grind the sample using a Wiley mill or similar equipment, precisely measure 20g of the powdered rice sample and put it into a 200ml Erlenmeyer flask with a plug.
2) Extracting of fat acid: Add 50ml of toluene and shake it for one minute. Extract fatty acid for 30 minutes with a shaker and one hour if a shaker is not used. Finish extraction by shaking for one minute.
3) Filtering: Filter it through folded filter paper. Take the first 25ml of the filtered solution, transfer it to the 100ml Erlenmeyer flask and add 25ml of phenolphthalein-ethyl alcohol solution (0.4g of phenolphthalein melted with 1l of 95% ethyl alcohol).
4) Titration and measurement: Titrate the solution with a 0.05N potassium hydroxide standard solution, and determine the fat acidity using the following equation;
Fat acidity (mgKOH/100g.d.w.) = (A ?B) x f x 2.805 x 100 x C / (S x D),
A : Titration value (ml) by 0.05N potassium hydroxide standard solution,
B : Blank value (ml),
f : Factor of 0.05N potassium hydroxide standard solution,
C : Volume of solution (ml) used for sample extraction,
S : mass of sample (g),
D : Volume of solution (ml) used for titration,
2.805 : mg value of potassium hydroxide contained in 1ml of 0.05N potassium hydroxide.