8. Characteristics of Rice Grain 1
- INDEX -
Physical Characteristics
Structure
Size, Shape and Color
Milky Kernel, White Belly Rice and White Core Rice
Endosperm Cell Arrangement
Physical Characteristics
Structure
Brown rice:
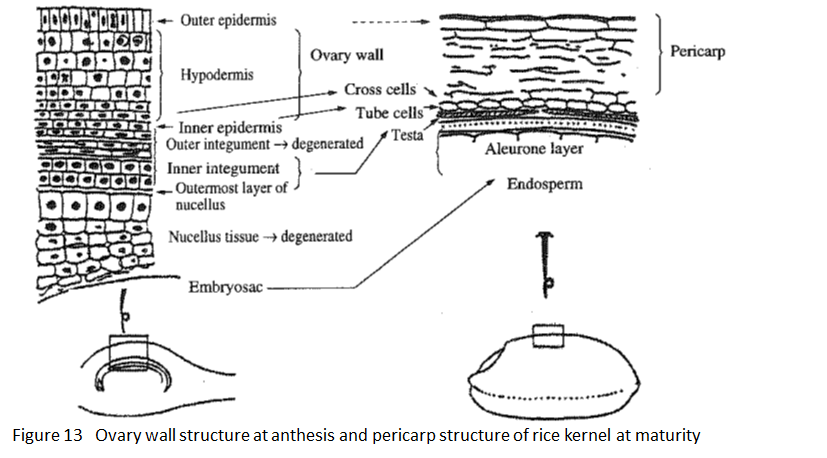
From the botanical point of view, the matured caryopsis is a seed. In terms of usage, however, it is a grain (paddy) for food. The paddy consists of hull and brown rice, and a brown rice consists, from its outer surface toward its center, of pericarp, testa, aleurone layers, endosperm and embryo, in this order. (Fig. 13)
Brown rice, as already explained, is mostly made of accumulated starch in cells within the embryosac.
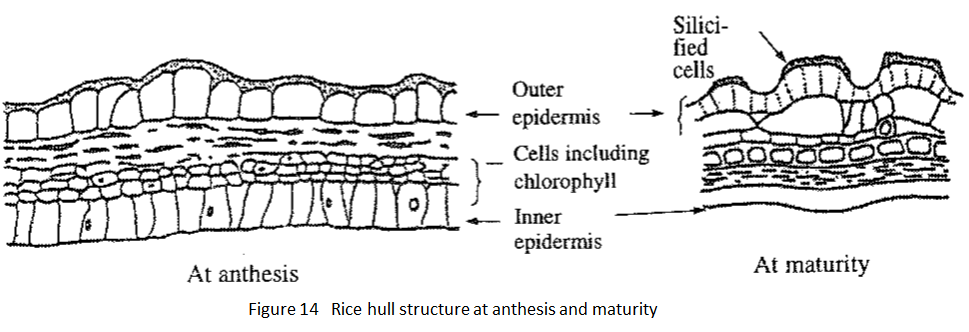
Rice hull:
The rice hull is a product of the very last process of young panicle differentiation. It consists of inner (palea) and outer (lemma) hulls and contains a large amount of silicic acid (Fig. 14). Some varieties have an awn at the distal tip of the outer hull, which, together with the color of the basal part, distinguish them from other varieties. The rice hull is also covered with short small hairs, which adversely affect the working environment of harvesting and processing by creating dust. Breeding efforts are being made to reduce these hairs, as well as the hairs at the surface of the leaf.